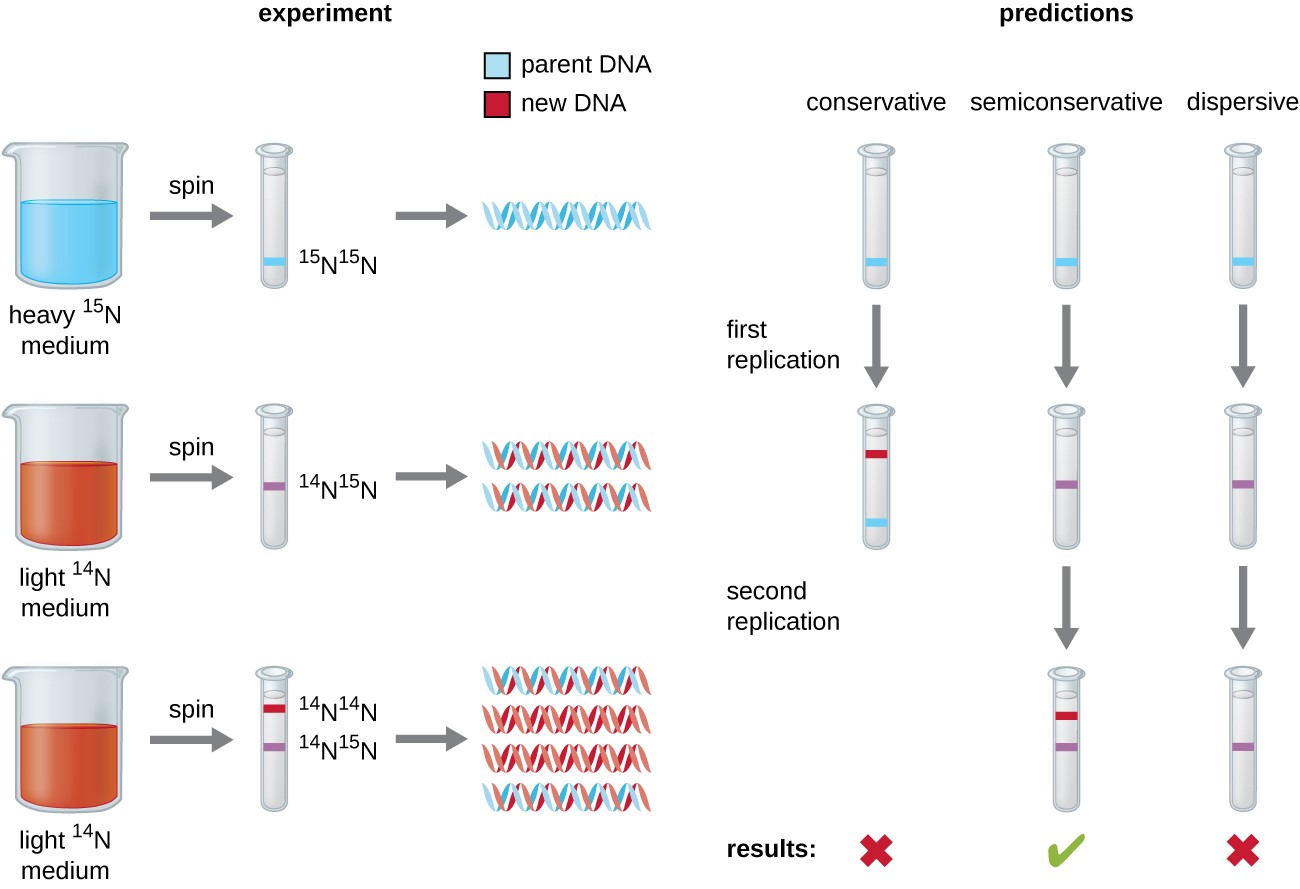
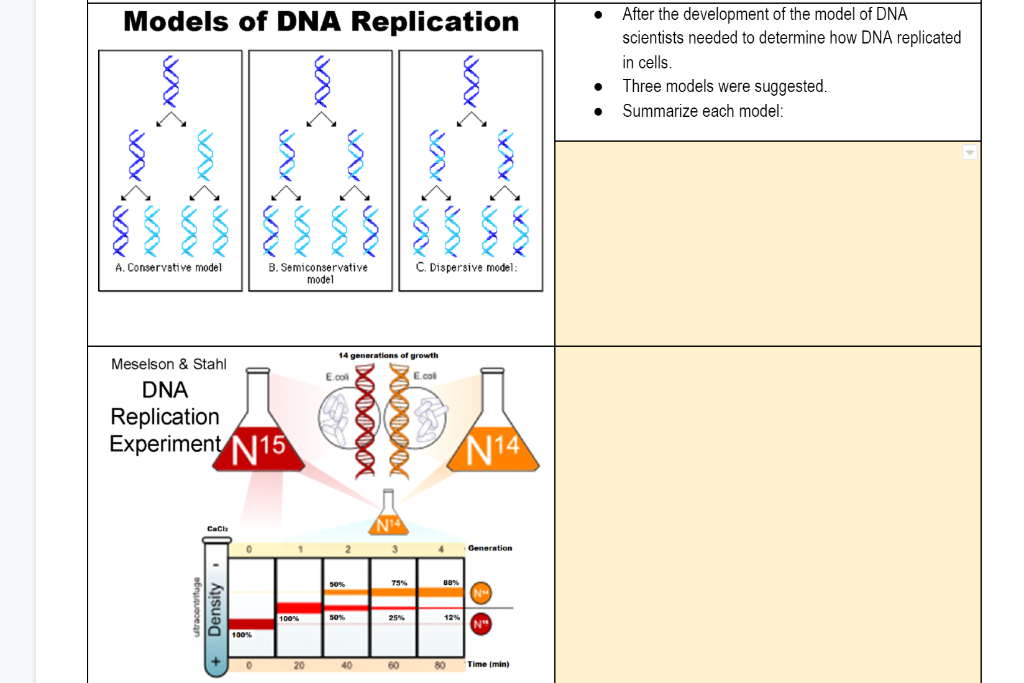
Conservative Model of Replication Sample 1 all DNA is 15N Sample 2 half of the DNA is 15N and half is 14N Sample 3 most DNA is 14N but some 15N remains 15N 14N 15N 15N 14N Predictions based on the Dispersive Model of Replication Sample 1 all DNA is 15N Sample 2 all of the DNA travels at the density of DNA that is half 15N and half 14N The dispersive model suggested that the two copies of the DNA would have segments of parental DNA and newly synthesized DNA The Meselson and Stahl experiment supported the semiconservative model of replication, in which an entire replicated chromosome consists of one parental strand and one newly synthesized strand of DNAWhat are the three models of DNA replication?
What Is The Semi Conservative Model In Dna Replication And Why Is It Important Quora
Dispersive model of dna replication
Dispersive model of dna replication-The dispersive DNA replication model presents cells with DNA strands broken down into fragments, dispersed in the cell, and then reunited to form the new strands The new strands appear like a patchwork containing fragments of the parental strands and new strands in a random mannerModes of replication Three proposed models of DNA replication are conservative, semi conservative and Dispersive Semiconservative here of the two newly formed strands one will be parental and other will be a newly synthesized strand Each parental strand serves as a template for the synthesis of daughter stands



Mode Of Dna Replication Meselson Stahl Experiment Article Khan Academy
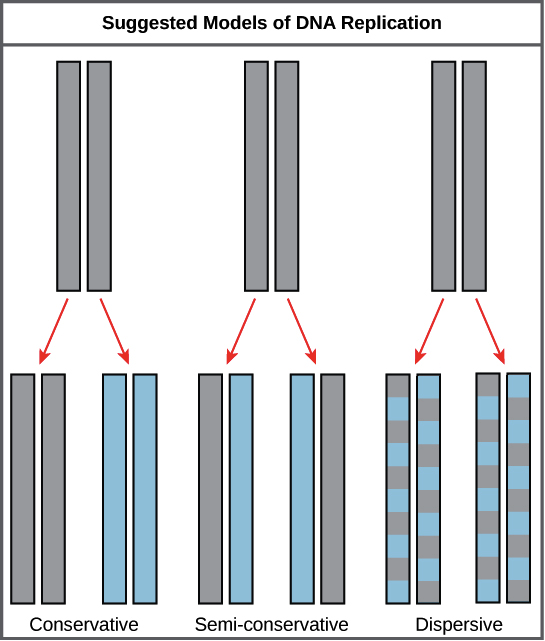
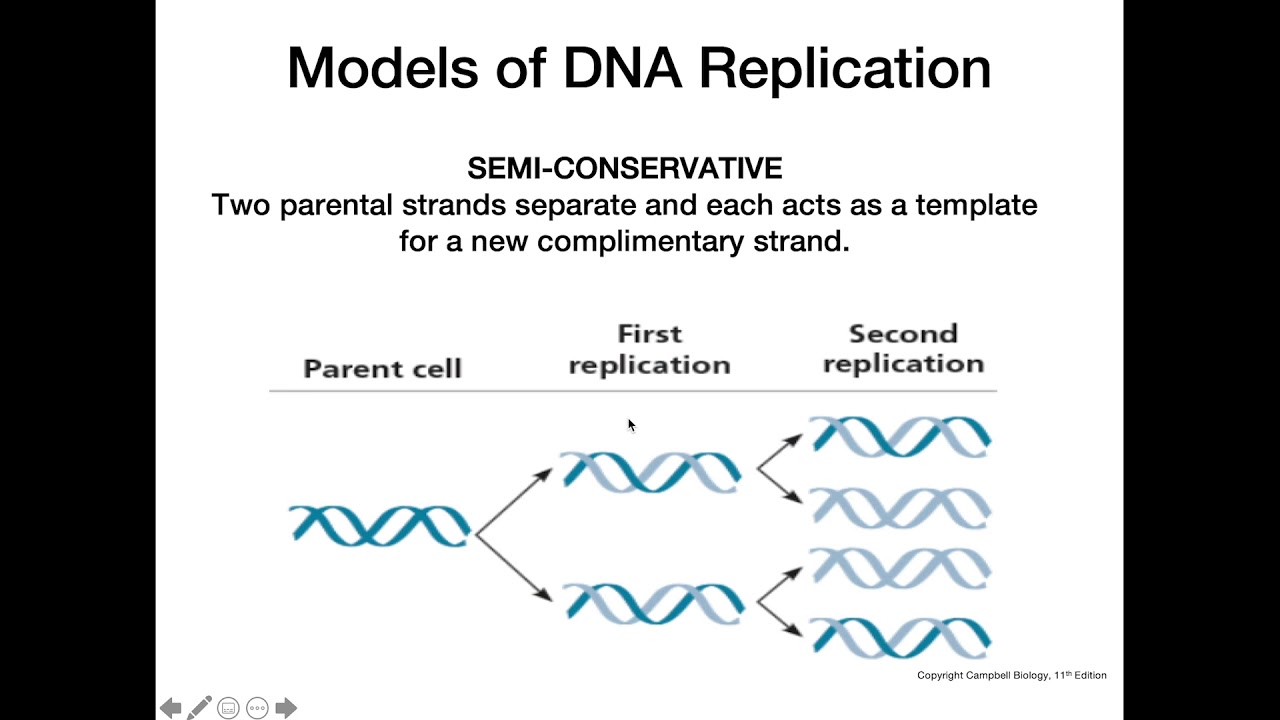
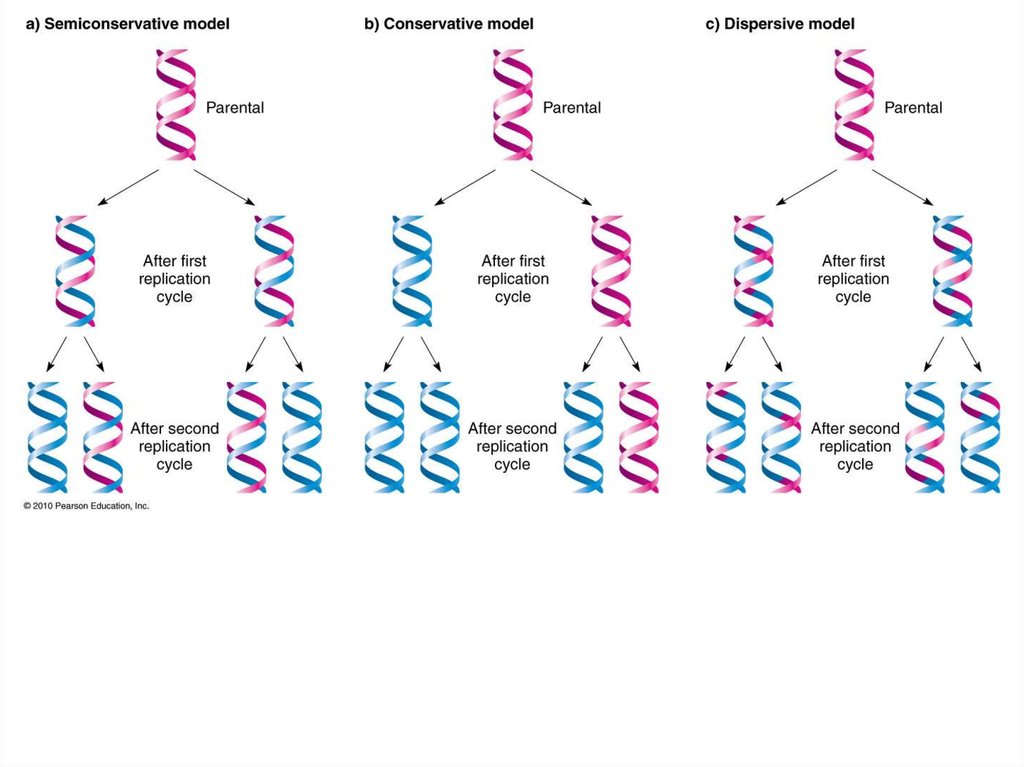
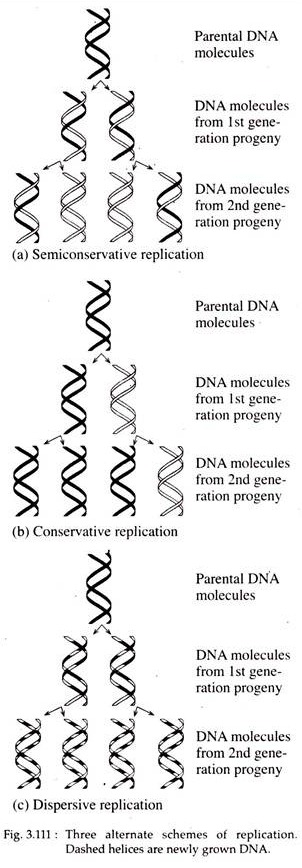
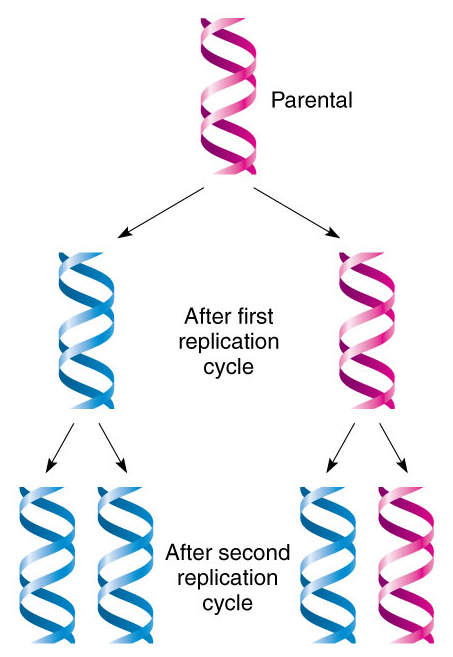
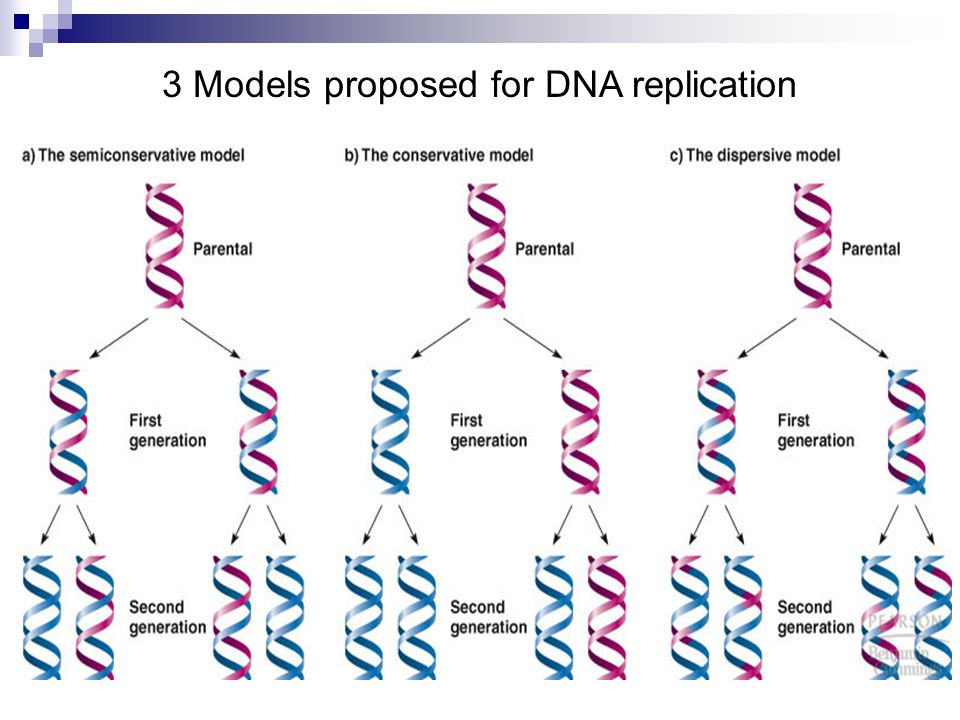
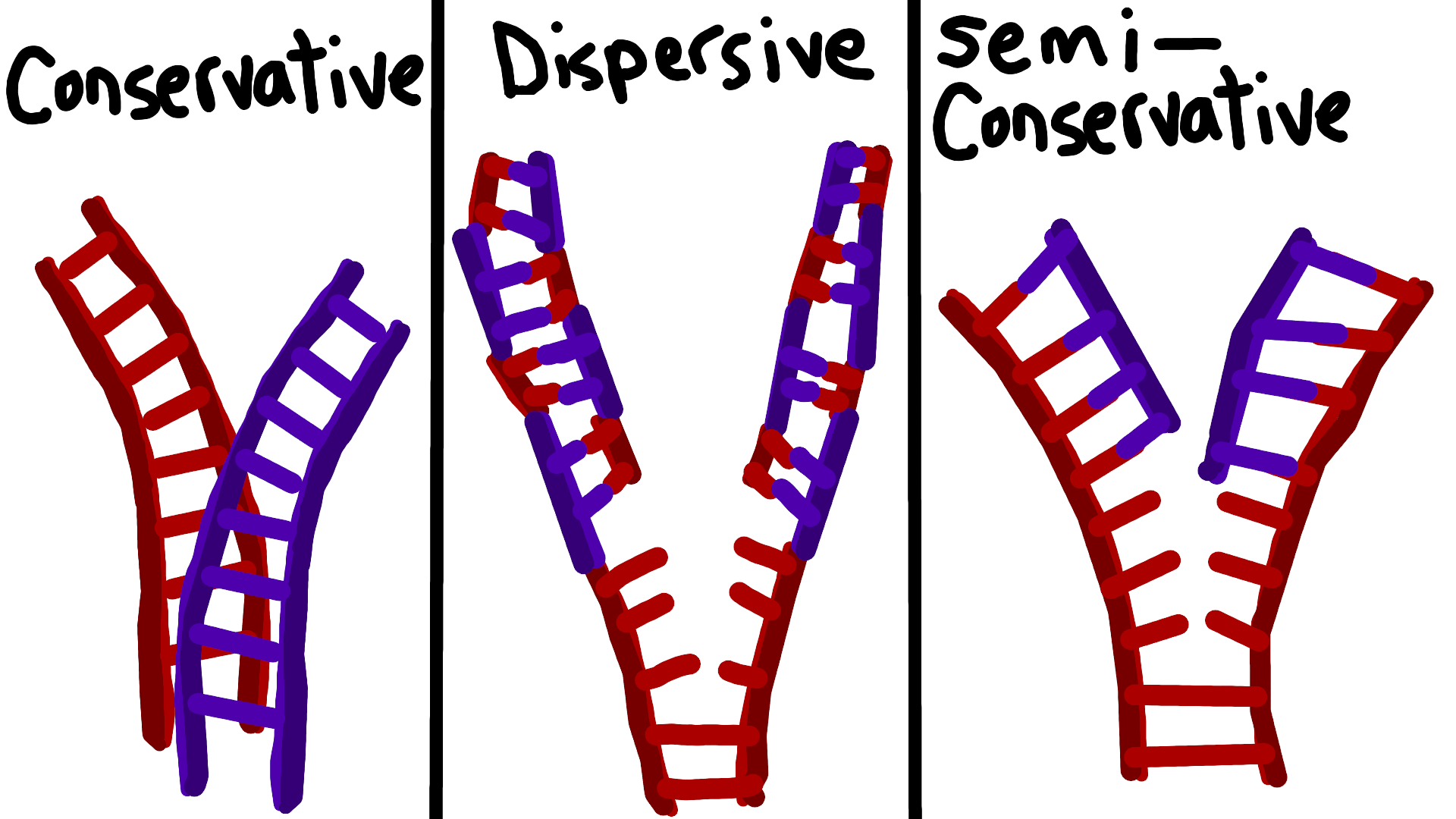
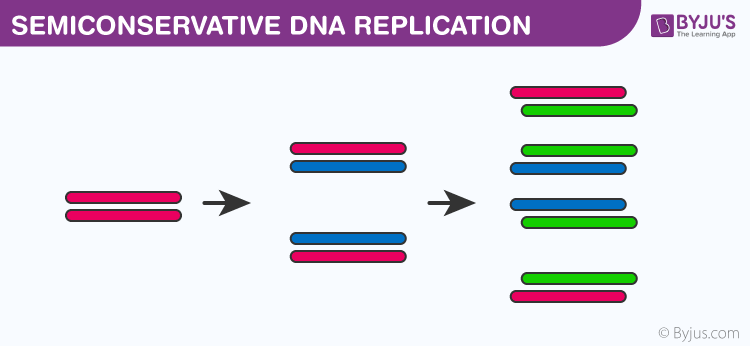
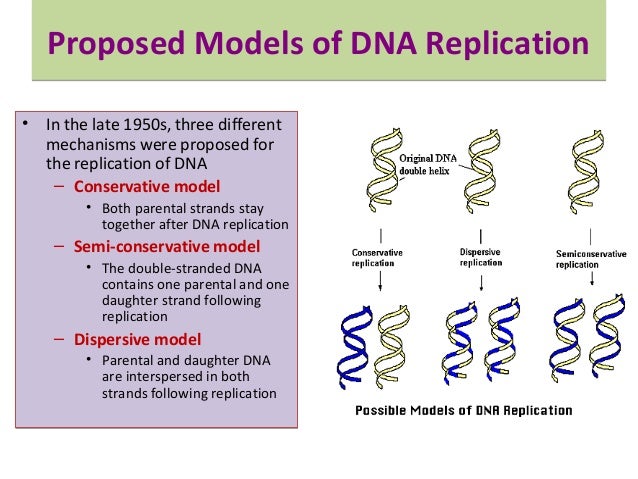
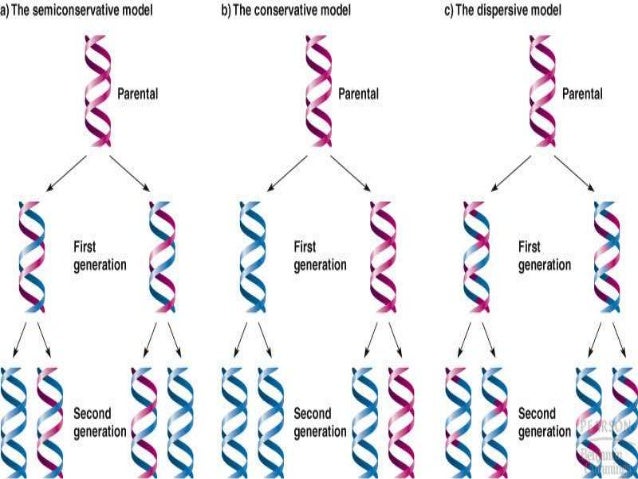
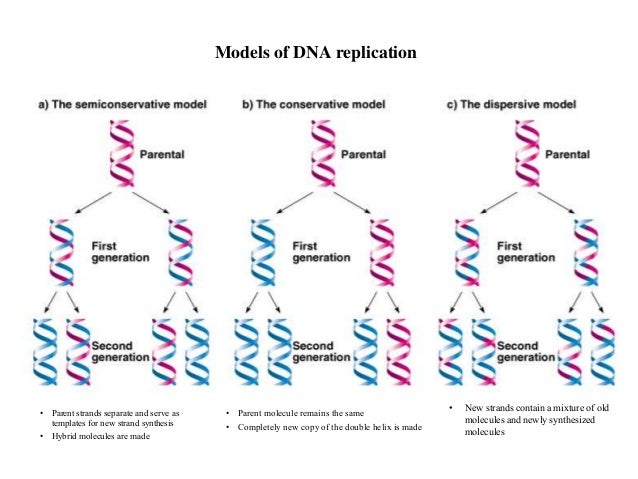
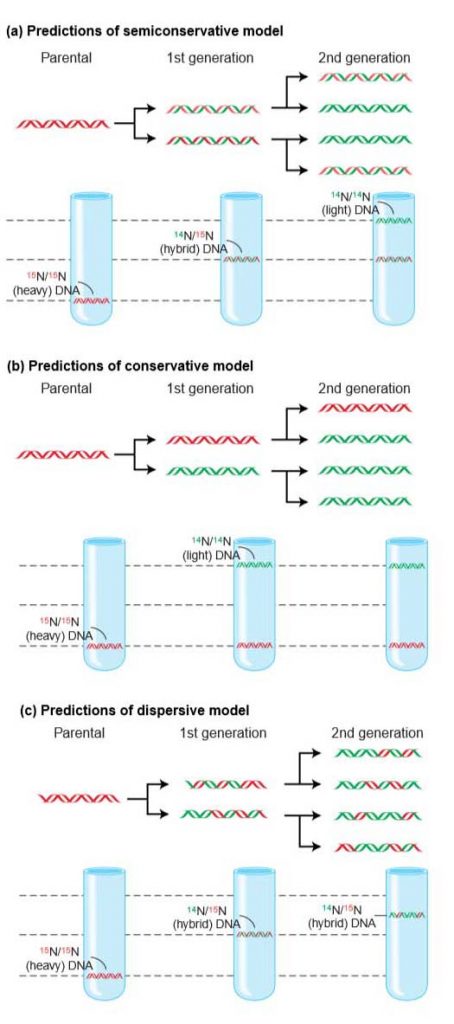
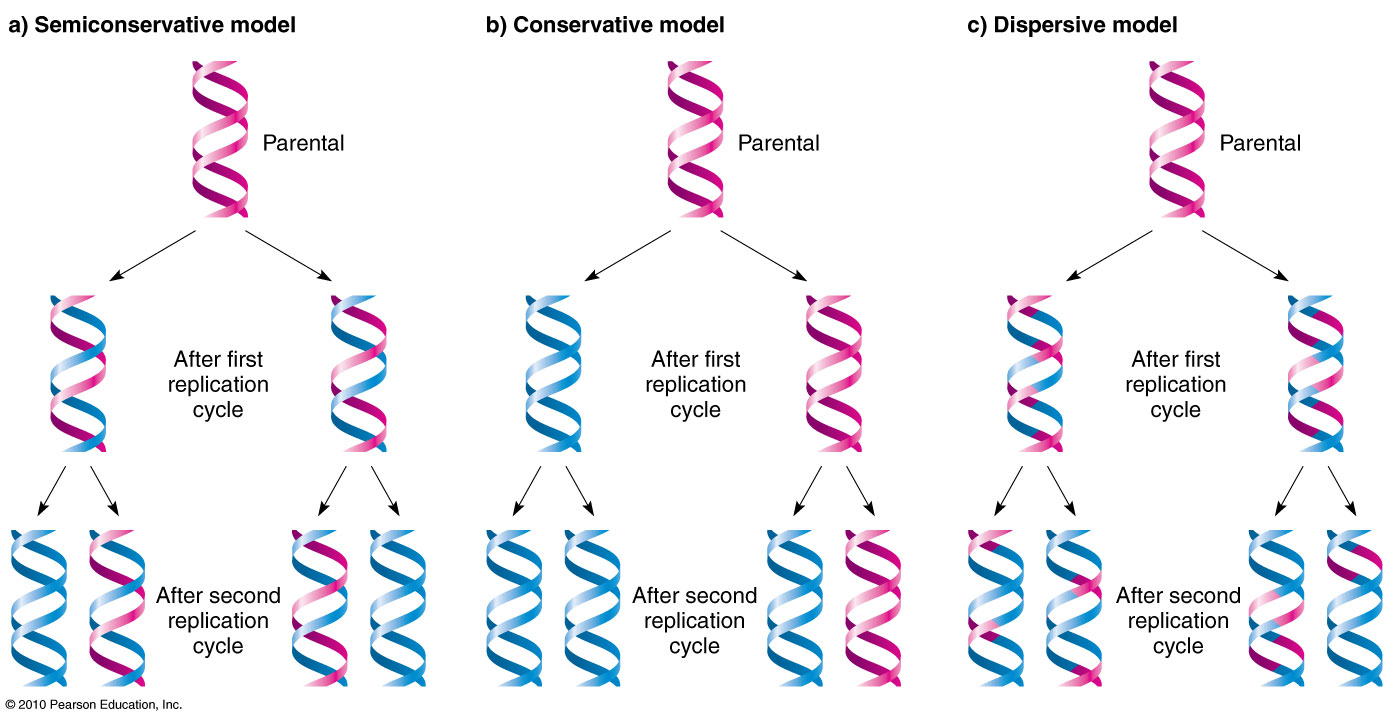
There were three models suggested ( Figure 1412 ) conservative, semiconservative, and dispersive Figure 1412 The three suggested models of DNA replication Gray indicates the original DNA strands, and blue indicates newly synthesized DNA In conservative replication, the parental DNA remains together, and the newly formed daughter strandsSemiConservative, Conservative, & Dispersive models of DNA replication In the semiconservative model, the two parental strands separate and each makes a copy of itself After one round of replication, the two daughter molecules each comprises one old and one new strandThus, each DNA molecule after replication would consist of one of the original strands plus one newly synthesized strand This model of DNA replication is called semiconservative Semiconservative was not the only model of DNA replication, however Other proposed models included conservative replication and dispersive replication
In the dispersive model of DNA replication, each strand of both daughter molecules contains a mixture of old and newly synthesized DNA Finally, using the colored DNA parental strands you have just created and the gray nucleotides, model the dispersive method of DNA replicationThere were three models for how organisms might replicate their DNA semiconservative, conservative, and dispersive The semiconservative model, in which each strand of DNA serves as a template to make a new, complementary strand, seemed most likely based on DNA's structureFigure DD1 A model for DNA replication proposed by Max Delbrück (later known as Dispersive Replication) DNA cuts (panel 2) are made along the double helix, and newly synthesized strands (blue) are rejoined to the original strands (purple) (panel 3), resulting in strands composed of alternating parent and newly copied DNA
The Meselson–Stahl experiment is an experiment by Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl in 1958 which supported Watson and Crick's hypothesis that DNA replication was semiconservativeIn semiconservative replication, when the double stranded DNA helix is replicated, each of the two new doublestranded DNA helices consisted of one strand from the original helix and one newlyDispersive DNA Replication In the dispersive model, material in the two parental strands is distributed more or less randomly between two daughter molecules In the model shown here, old material is distributed symmetrically between the two Dispersive replication is the third possible model of DNA replication The model produces DNA helices that contain a mixture of old and new DNA Thus, each new strand in the helix is a patchwork of old and new DNA In simple words, all strands in the DNA helices contain alternating parental and new DNA segments, as explained in this model



1




How Dna Replicates Matthew Meselson Franklin W Stahl Genetics How Dna Replicates
(genetics) A model of DNA replication in which two new DNA molecules are produced containing regions of either both orig molecule and a newly made strand This is referred to as semiconservative replication It can be distinguished from a conservative model of replication in which the two parental strands come back together and the new daughter molecule is made up of two new strands A third model, dispersive replication, predicts that the two daughterFigure 41 Three possible models of DNA replication DNA from the original double helix is blue;




Dna Replication Recombination Chapter 12 Flashcards Quizlet



Watson Crick Model For Dna Replication Is Given Below Identify The Mode Of Replication By Selecting The Option Img Src D10lpgp6xz60nq Cloudfront Net Physics Images Grb Obj Bio Iind C54 E01 3 Q01 Png Width 80
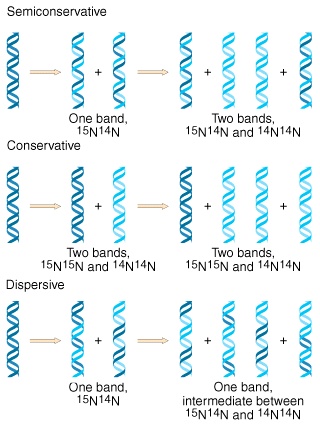
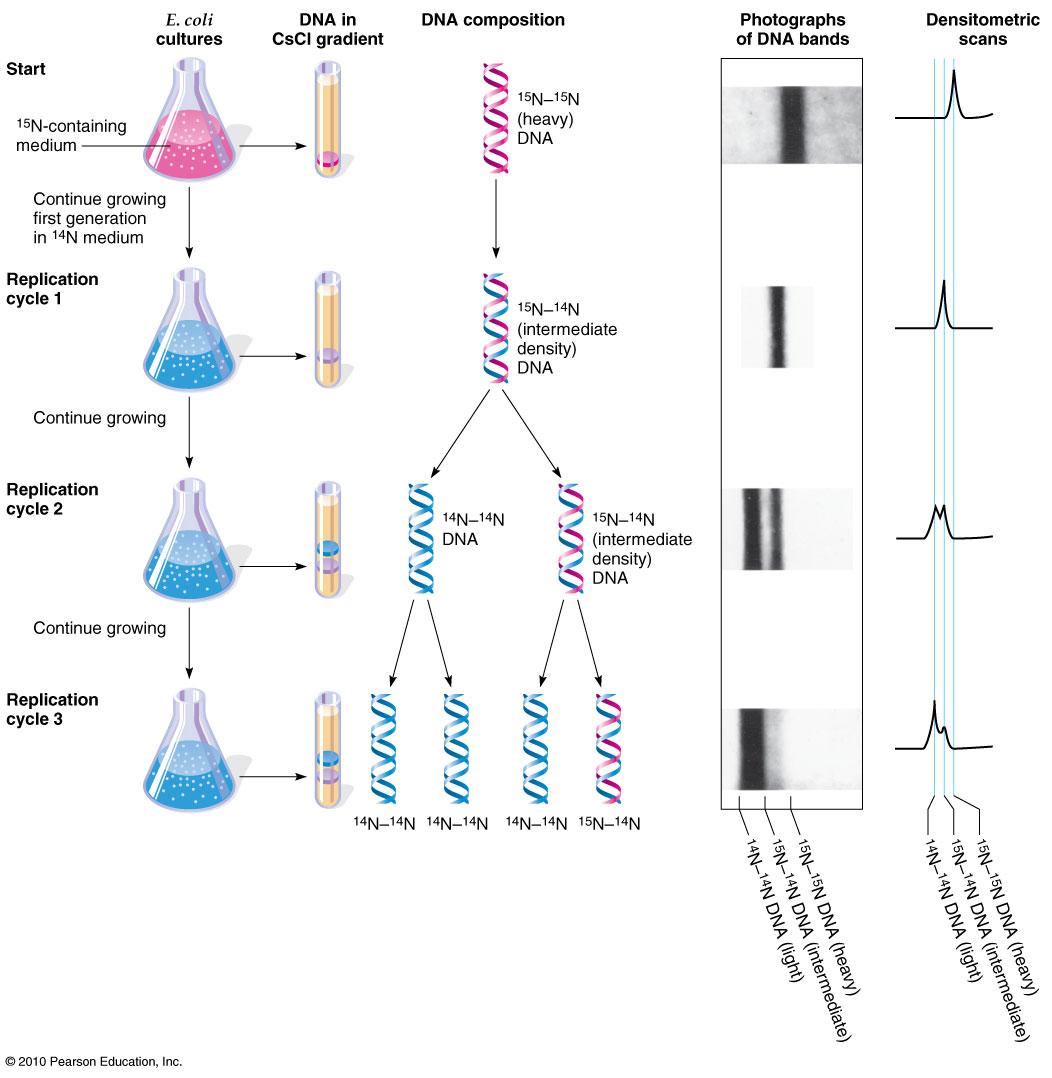
Explain what semiconservative DNA replication is and how it is different from conservative and dispersive models of DNA replication6 Name the five major enzymes involved in DNA replication and briefly explain their roles in the process7 Discuss the differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell division and DNA replicationThe Conservative Replication Model Biology Essay In the dispersive replication model, the original DNA double helix breaks apart into fragments and each fragment then serves as a template for a new DNA fragment As a result, every cell division produces two cells with varying amounts of old and new DNAIn the dispersive model of DNA replication, each strand of the daughter DNA molecule is a mixture of old and newly synthesized DNA pieces If the pieces were all the same size, then a single intermediate band would be present in the first generation After another round of replication, more 14 N would have been incorporated, giving rise to a




Molecular Lecture 4 Dna Replication Flashcards Quizlet




Mode Of Dna Replication Meselson Stahl Experiment Article Khan Academy
The dispersive model suggested that the two copies of the DNA would have segments of parental DNA and newly synthesized DNA The Meselson and Stahl experiment supported the semiconservative model of replication, in which an entire replicated chromosome consists of one parental strand and one newly synthesized strand of DNA Dispersive replication In the dispersive model, DNA replication results in two DNA molecules that are mixtures, or "hybrids," of parental and daughter DNA In this model, each individual strand is a patchwork of original and new DNAThere were three models suggested conservative, semiconservative, and dispersive The three suggested models of DNA replication Grey indicates the original DNA strands, and blue indicates newly synthesized DNA In conservative replication, the parental DNA remains together, and the newly formed daughter strands are together



Dna Replication Models Youtube



Dna Replication Rna Structure Function And Compare Dna Rna Prezentaciya Onlajn
3) Dispersive DNA replication model In dispersive mechanism, the parental DNA strands are fragmented and they combine with the newly synthesized segments to generate DNA duplexes, in which each strand is a hybrid of the parental segment and newly formed segmentAnswer After the discovery of Double helical structure of DNA by Watson and Crick, there were 3 different models regarding DNA replication proposed by scientists, those are 1 Conservative, 2 Semiconservative and 3 Dispersive 1 According to Conservative model ofNewly made DNA is magenta (a) Semiconservative replication (the WatsonCrick model) (b



Dna Replication Modes Ingredients And Ingredients




Meselson And Stahl Designed An Experiment That Would Allow Them To Discern Whether Dna Replication Brainly Com
Theoretically, there are the following three possible modes of DNA replication (1) Dispersive, (2) Conservative and ADVERTISEMENTS (3) Semiconservative 1 Dispersive Replication In dispersive replication, the parent DNA molecule is broken into several pieces, and the 'new' molecules will consist of both old and newly synthesized segmentsConservative model of DNA According to this model the parental DNA will be conserved in the next generation For example, a cell containing a double stranded parental DNA (represented by black color) will divide by mitosis into two daughter cells Now, one daughter cell will contain the parental doubleAfter Watson and Crick proposed the double helix model of DNA, three models for DNA replication were proposed conservative, semiconservative and dispersive Conservative Model In this model the two parental DNA strands are back together after replication has occurred Semiconservative Model Dispersive Model



Legacy Genetics Gsa Org



Dna Replication Advanced Ck 12 Foundation
One we use today c Dispersive model – new DNA is dispersed throughout each strand of both daughter molecules after replication 11 DNA replication a Requires 3 things i Something to copy 1 Parental DNA molecule ii Something to do the copying 1 Enzymes iii Building blocks to make copy 1 Nucleotide triphosphates 12 Stages of DNADispersive DNA replication Semiconservative DNA replication model Watson & Crick suggested the 'Semi conservative DNA replication' model According to this model, the two strands of DNA separate Each strand act as template for synthesis of a new strand The new strand is synthesized based on complementary base pairing with the templateAfter Watson and Crick proposed the double helix model of DNA, three models for DNA replication were proposed conservative, semiconservative and dispersive Conservative Model In this model the two parental DNA strands are back together after replication has occurred Semiconservative Model



Today 1 Dna Replication 2 Protein Synthesis 3 Dna Structure Ppt Download



Dna Replication Microbiology
Immediate after the structural conformation of DNA using Xray crystallography Watson and Crick proposed the mode of transfer is semiconservative And this is proved by the Meselson and Stahl experiments Description of Different Modes of Transfer 1 Conservative Modes of Transfer In the Conservative model of DNA replicationDispersive replication suggested that each DNA molecule after replication might consist of segments of new and old DNA interspersed It would be difficult to devise a mechanism by which this latter outcome might occur, but until evidence to the contrary was produced, it had to be considered The three possible models of DNA replication are In dispersive replication, DNA is copied in short chunks, and the result is a molecule that alternates pieces of parent DNA with daughter DNA After one replication, the new molecule would be 50%



Replication Of Dna Conservative Dispersive And Semiconservative




Dna Replication Advanced Ck 12 Foundation
After ONE round of DNA replication in Meselson and Stahl's classic experiment, _____ a) the dispersive model was conclusively proven to be an inaccurate model b) the semiconservative model was conclusively proven to be the accurate model c) the conservative model was conclusively proven to be an inaccurate modelThe model that Watson and Crick proposed in 1953 to describe the molecular structure of DNA was a landmark discovery But at the time, many scientists weren'In Summary Basics of DNA Replication The model for DNA replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is copied In conservative replication, the parental DNA is conserved, and the daughter DNA is newly synthesized
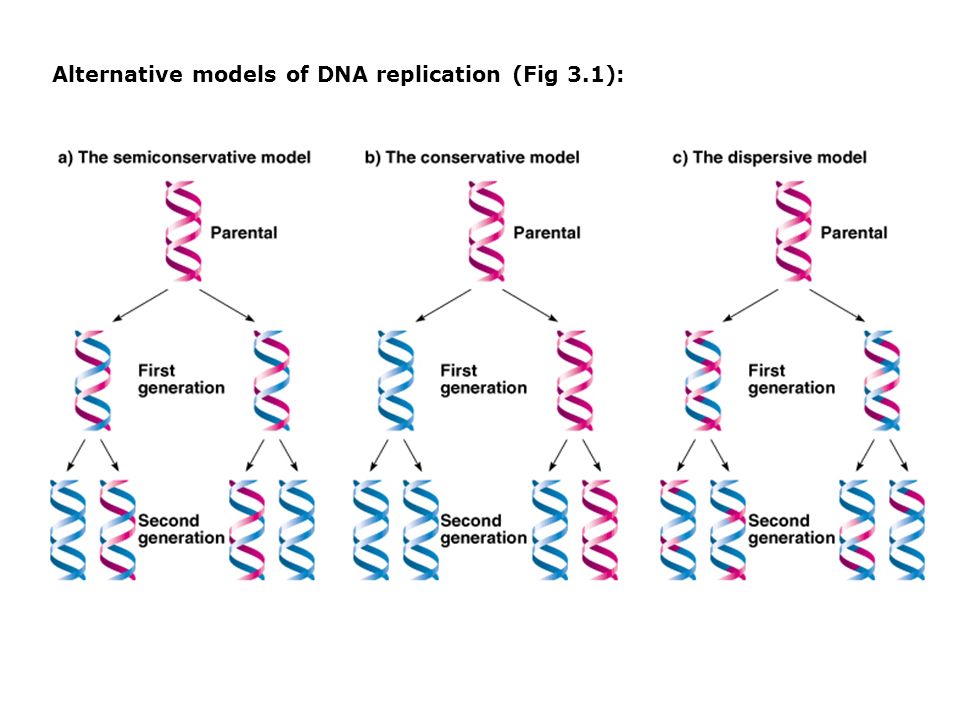



Alternative Models Of Dna Replication Fig 3 1 Ppt Video Online Download
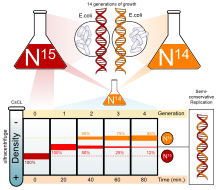



Semiconservative Replication Wikipedia
What does dispersivemodel mean?So, DNA replication occurs within a forklike structure in which the lagging strand loops around in a proposed "trombone model" to orient the replication enzymes for repeated synthesis and joining It is considered that this mechanism helps to maintain the integrity of DNA during the replication cyclesDelbrück's dispersive replication, presented in "On the Replication," provided a plausible counterexample to the semiconservative model of replication While many accepted the WatsonCrick replication mechanism initially, Delbrück's article showed that questions regarding DNA replication were far from answered
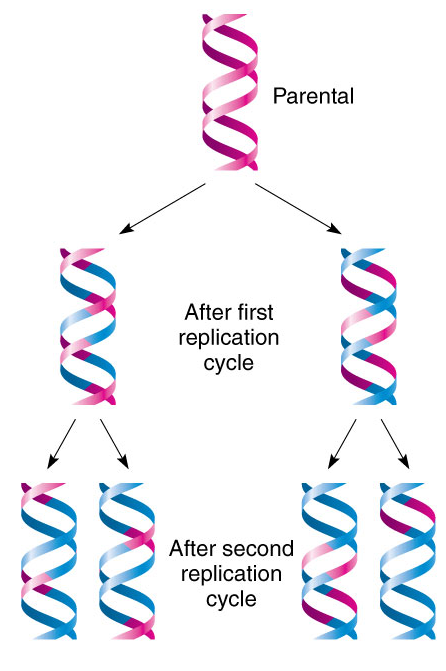



Replication Of Dna Conservative Dispersive And Semiconservative



Difference Between Conservative And Semiconservative Replication Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
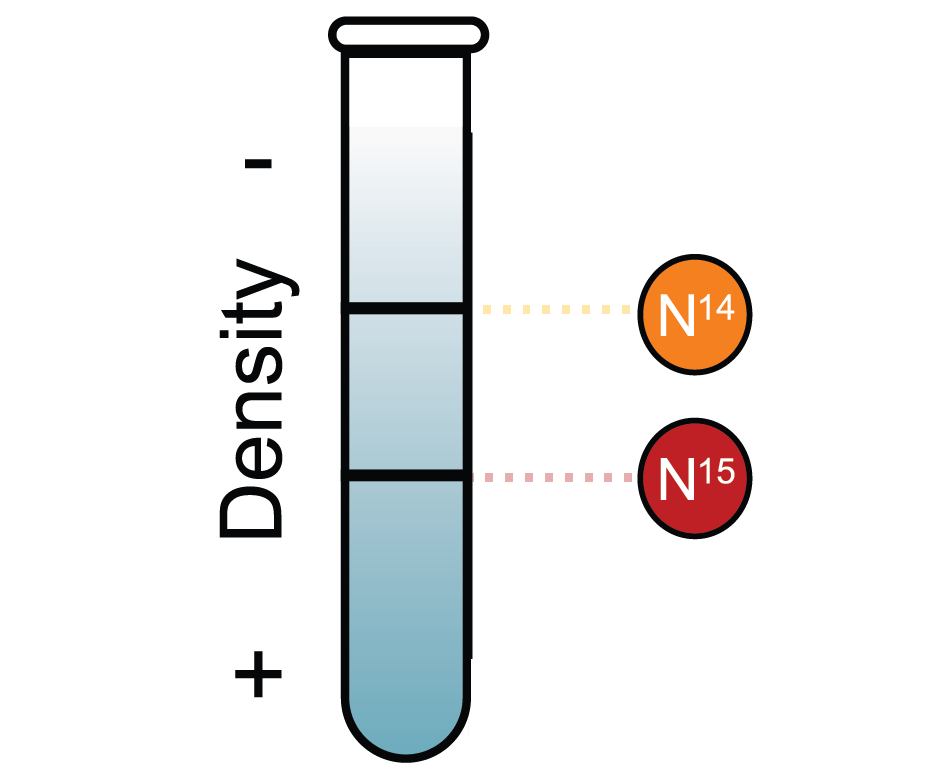
Dispersive Replication In this hypothesis, it is proposed that the original molecule is broken into fragments Each fragment serves as a template for the synthesis of complementary fragments and finally, two new molecules are formed which consist of both old and new fragmentsDispersive model parental and daughter DNA segments are interspersed in both strands following replication Meselson and Stahl experiment 1) add an excess of 14Ncontaining compounds to the growth medium so all of the newly made DNA will contain 14N 2) Incubate the cells for various lengths of time in 15N 3)The dispersive model suggested that the two copies of the DNA would have segments of parental DNA and newly synthesized DNA The Meselson and Stahl experiment supported the semiconservative model of replication, in which an entire replicated chromosome consists of one parental strand and one newly synthesized strand of DNA
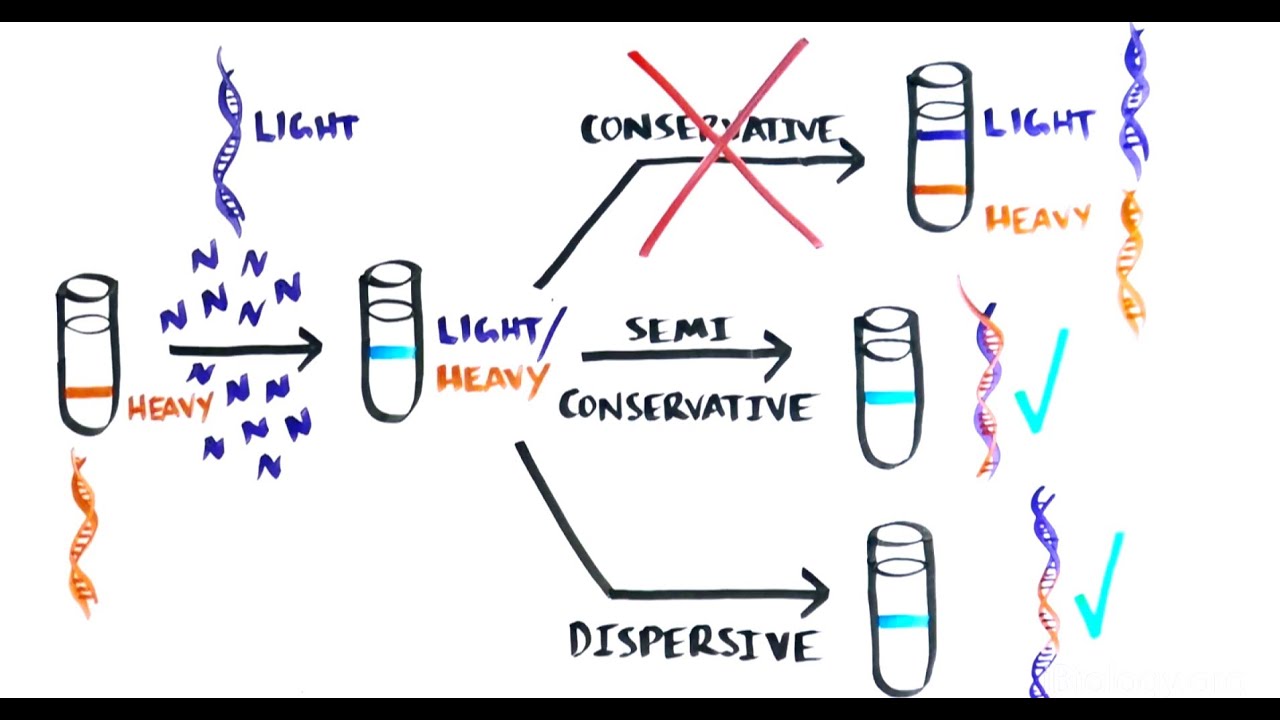



The Most Beautiful Experiment In Biology Meselson Stahl The Semi Conservative Replication Of Dna Youtube




The Molecular Basis Of Inheritance Prezentaciya Onlajn
Delbrück suggested a new model of DNA replication in a 1954 article, a model later called dispersive DNA replication Delbrück argued that if each strand of DNA potentially serves as a template for a new strand during replication, like the Watson and Crick model theorized, then there could only be three ways to separate the DNA strandsModels of DNA Replication1 Conservative2 Dispersive3 Semi conservativeThere were three models suggested conservative, semiconservative, and dispersive The three suggested models of DNA replication Grey indicates the original DNA strands, and blue indicates newly synthesized DNA In conservative replication, the parental DNA remains together, and the newly formed daughter strands are together




Dna Replication Conservative Semi Conservative And Dispersive Methods



Csun Edu
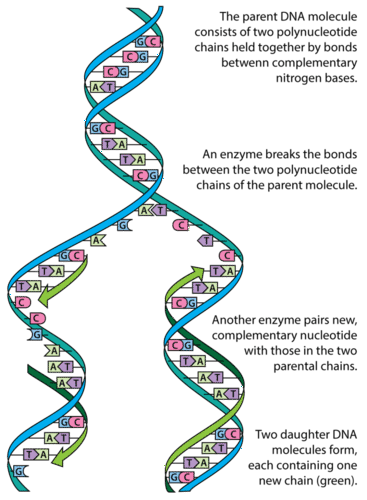
Dispersive replication A form of DNA replication in which the original DNA chain breaks and recombines in a random fashion before the double helix structure unwinds and separates to act as a template for messenger RNA synthesis There is no evidence that it occurs in nature Source for information on dispersive replication A Dictionary of Biology dictionaryT/F The data obtained from the MeselsonStahl experiment after one generation of replication eliminated the dispersive model of DNA replication False Which enzyme catalyzes the addition of nucleotides to a growing DNA chain? Literally, replication means the process of duplication In molecular biology, DNA replication is the primary stage of inheritance Central dogma explains how the DNA makes its own copies through DNA replication, which then codes for the RNA in transcription and further, RNA codes for the proteins by the translation




L14 Modes Of Dna Replication Conservative Semi Conservative Dispersive Youtube



Authored By Peter J Russell Ppt Download
Dispersive model of DNA replication;



Mastering Your Way To Med School Bio 1000 Dna Replication




Cmb Chapter 6 Dna Replication Repair Recombination Flashcards Quizlet




Final Bio 1610 Flashcards Quizlet



Conservation Of Genetic Material Dna Replication Expii



Modes Of Replication



C05 F2401 06 Lecture 11



The Meselson And Stahl Experiment On Dna Replication



Mode Of Dna Replication Meselson Stahl Experiment Article Khan Academy
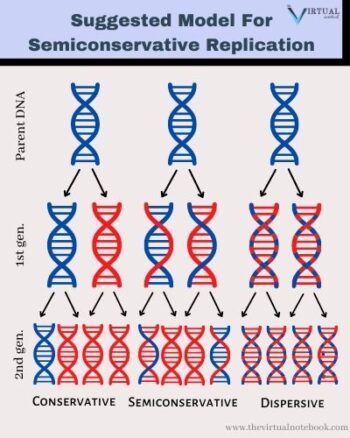



Dna Replication Is Semiconservative The Virtual Notebook



Difference Between Conservative And Semiconservative Replication Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms




A Schematic Showing Single Units Of The Kshv Tr And The Sequence Of Download Scientific Diagram




Dna Replication Steps Know 3 Steps Of Dna Replication In Simple Terms




What Is Dna Replication Conservative Semi Conservative Dispersive Models Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Modes Of Replication




What Is Semi Conservative Dna Replication How Was It Experimentally Proved And By Whom



How Dna Replicates Matthew Meselson Franklin W Stahl Genetics How Dna Replicates



Models Of Dna Replication Notes With Definition Diagram Readbiology Com



Dna Replication




Semiconservative Replication And Meselson And Stahl Experiment Biotechfront




I Really Need Help With Understanding Dna Semiconservative Replication R Mcat




Broad Course Objectives For Dna Replication Students Will



Dna Replication In Cells




7 3a Basics Of Dna Replication Biology Libretexts




Solved Copy Of Tested Student Outcome Describe The Chegg Com




Great Experiments The Method Of Dna Replication Discussed Oct 12



What Is The Semi Conservative Model In Dna Replication And Why Is It Important Quora
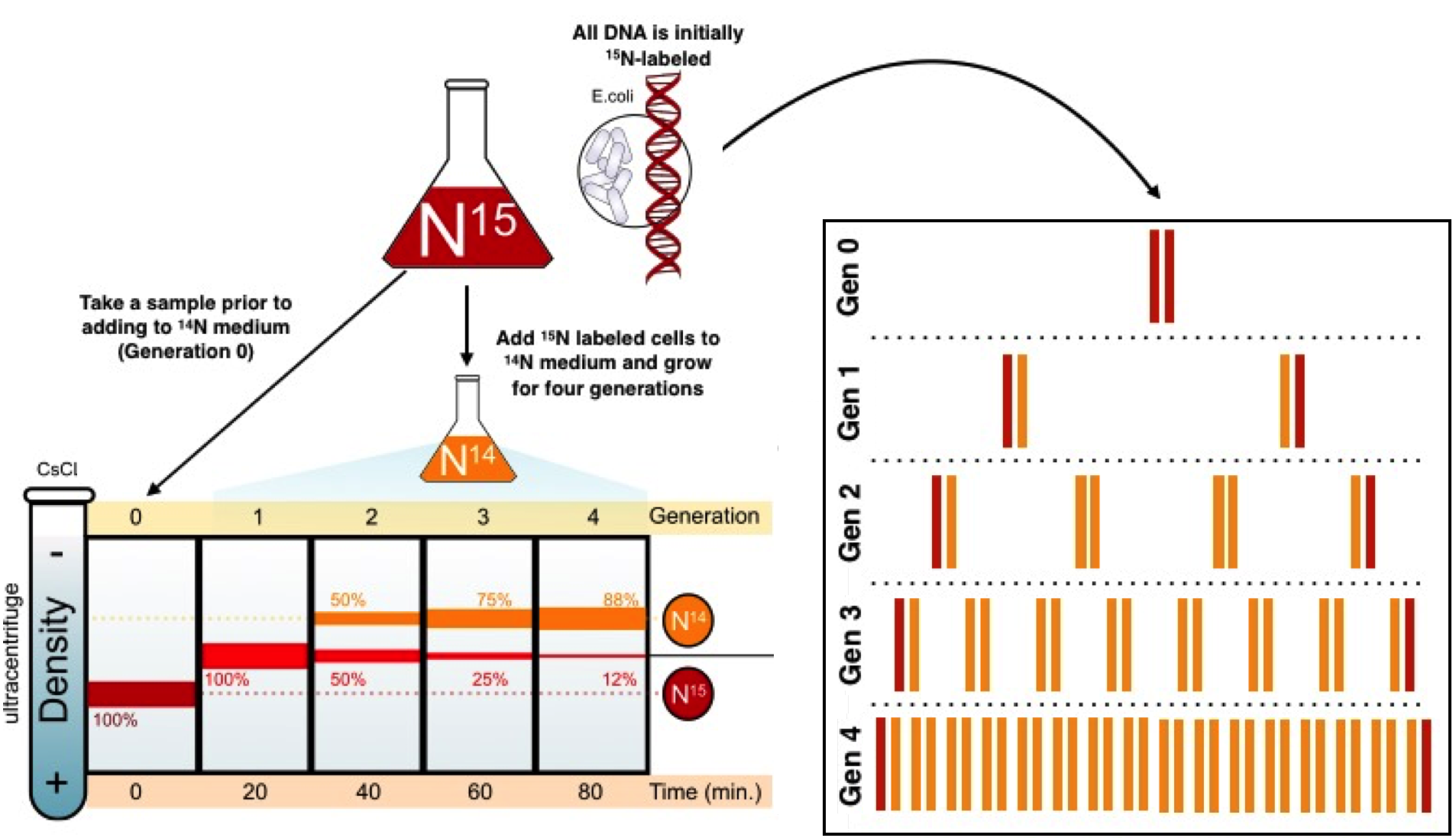



Mode Of Dna Replication Meselson Stahl Experiment Article Khan Academy




Three Alternative Models Of Dna Replication Worksheet
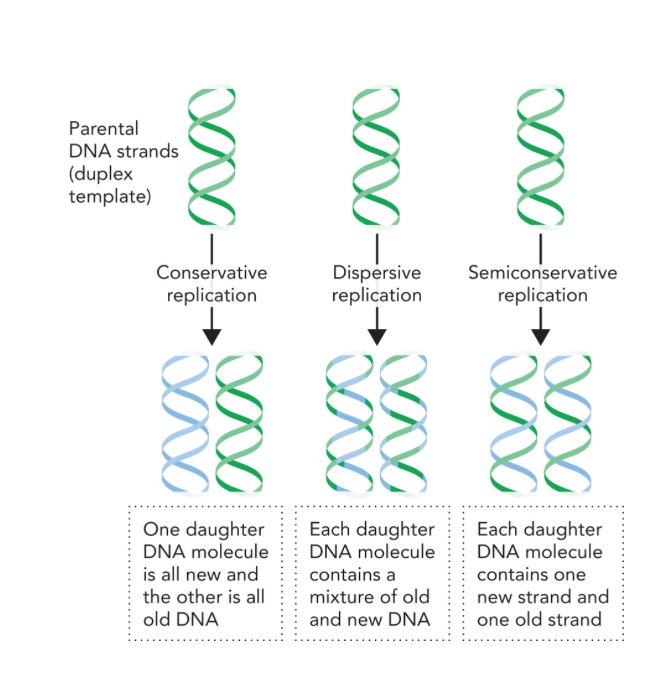



Solved Which Model Of Dna Replication Would Require Chegg Com
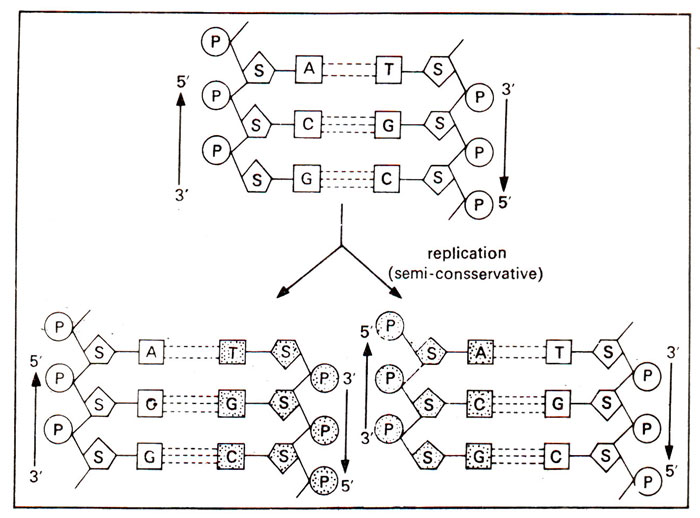



Semi Conservative Dna Replication In E Coli




How Dna Replicates Matthew Meselson Franklin W Stahl Genetics How Dna Replicates



Dna Replication




What Is Meant By The Semiconservative Natu Clutch Prep



Programming For Lovers Chapter 1 Phillip Compeau




7 2 Semi Conservative Dna Replication Biology Libretexts




Semi Conservative Bioninja



Gr08 13



Replication




Learn About Semiconservative Replication Dna Chegg Com



Csun Edu




1 Dna Replication Models Pj Russell Igenetics 3rd Ed 10 Download Scientific Diagram



Difference Between Conservative Semiconservative And Dispersive Replication Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms



Prezentaciya Na Temu Dna Replication In Molecular Biology Dna Replication Is The Biological Process Of Producing Two Identical Replicas Of Dna From One Original Dna Molecule Skachat Besplatno I Bez Registracii



S3 Studentvip Com Au



Dna Replication



Meselson Stahl Experiment Study Solutions




Semi Conservative Bioninja




Dna Replication Microbiology



The Meselson Stahl Experiment




Density Matters The Semiconservative Replication Of Dna Pnas



Modes Of Dna Replication



Semi Conservative Replication



Conservation Of Genetic Material Dna Replication Expii



Legacy Genetics Gsa Org



Dls Ym Edu Tw



What Is The Semi Conservative Model In Dna Replication And Why Is It Important Quora




Dna Replication Conservative Semi Conservative And Dispersive Methods



S3 Studentvip Com Au



3



Solved O Models Of Dna Replication After The Development Of Chegg Com



Semiconservative Model Of Dna Replication Competitors Point




Dna Replication Advanced Ck 12 Foundation



What Is The Importance Of Semiconservative Replication Of Dna Quora




Conservation Of Genetic Material Dna Replication Expii
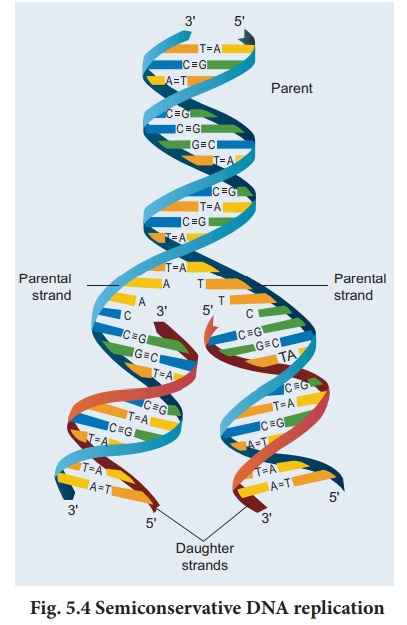



Dna Replication Molecular Genetics




Dna Replication A Dna Replication Is Semiconservative B Dna Replication In E Coli C Dna Replication In Eukaryotes Chapter Ppt Download
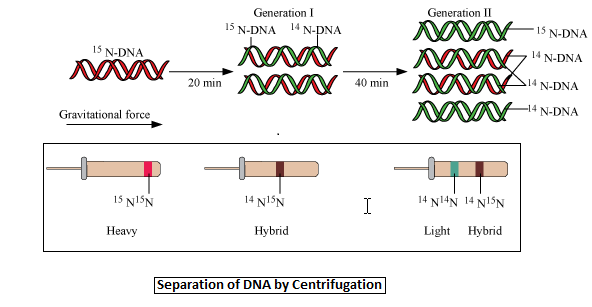



The Experimental Proof For Semiconservative Replication Class 12 Biology Cbse



Dna Replication A Closer Look




What Is Dna Replication Conservative Semi Conservative Dispersive Models Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Flow Of Genetic Information Kit Replication Activity Guide Student Handout And Key




How Dna Replicates Matthew Meselson Franklin W Stahl Genetics How Dna Replicates




Biology Ict For Meaningful Learning




The Data Obtained From The Meselson Stahl Experiment After One Generation Of Replication Eliminated Brainly Com




Structural Biochemistry Nucleic Acid Dna Meselson Stahl Experiment Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World



American Board



1



1




Lecture Series 6 Dna And Its Role In



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿